Table of Contents
ToggleA Comprehensive Guide to LED Wattage Equivalents
Understanding LED equivalent power helps you choose right wattage when replacing traditional lighting.
LED equivalent chart :
Note: The following is just an estimate, the specific decision should be based on the LED luminous efficiency.
| LED Wattage | Incandescent Equivalent | Fluorescent Equivalent | Halogen Equivalent | Luminous Flux (lm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5W | 40W | 10W | 30W | ~450 lm |
| 9W | 60W | 15W | 50W | ~800 lm |
| 12W | 75W | 20W | 60W | ~1100 lm |
| 15W | 100W | 25W | 80W | ~1600 lm |
What Does LED Light Bulb Wattage Mean?
In traditional light bulbs like halogen and incandescent, wattage directly indicates brightness. However, with LED, wattage measures energy usage, while lumens quantify brightness.
led light bulb wattage directly affects electricity bills, but it doesn’t necessarily reflect brightness; brightness is determined by lumens (lm). The higher the LED’s luminous efficacy (lm/W), the more lumens it produces at the same wattage, resulting in a brighter light.
LED vs Incandescent Bulb Wattage: A Science
After conversion from incandescent to LED, energy saving can reach over 80%. LED deliver the same brightness as tungsten bulbs or incandescent light bulbs while consuming only a fraction of the energy, making them highly efficient. For example:
- A 60W incandescent bulb is equivalent to a 9W LED.
- A 100W incandescent bulb is equivalent to an 18W LED.

LED Light Bulb Wattage and Lumens
Because LED technology differs from conventional incandescent bulbs, switching to LEDs often raises concerns about wattage. To achieve the same brightness (lumens), LED lights use significantly less energy (watts).
In this article, we’ll break down various LED watt equivalents, such as 8W, 15W, 40W, 60W, 75W and 100W LED bulbs, to help you choose the best bulb for your needs. We’ll also highlight LedRhythm’s lighting products, which combine cutting-edge technology with exceptional energy efficiency.
The conversion from watts to lumens is determined by the luminous efficacy (lm/W), which varies greatly between models and brands.
For example, conversion chart watts to lumens for 80-120 lm/W:
| LED Power (W) | Luminous Flux Range (lm) | Equivalent Incandescent Bulb Power (Approx) |
|---|---|---|
| 5W | 400 – 600 lm | ≈ 45W – 55W |
| 8W | 640 – 960 lm | ≈ 65W – 85W |
| 10W | 800 – 1200 lm | ≈ 80W – 100W |
| 15W | 1200 – 1800 lm | ≈ 110W – 150W |
| 20W | 1600 – 2400 lm | ≈ 140W – 180W |
LED Wattages for Common Types of Bulbs
8 Watt LED Equivalent
An 8W LED light is approximately as bright as a traditional 60W incandescent. The average brightness is 800lm.
15W LED Equivalent
The average brightness of 15W LED light over 1500lm.
Therefore, 15W LED can completely replace a traditional 100W incandescent and save about 85% of energy.
40W LED Equivalent
A 5W-7W LED bulb replaces a 40W incandescent bulb, delivering the same brightness while using far less energy.
Ideal for accent lighting or task lighting.
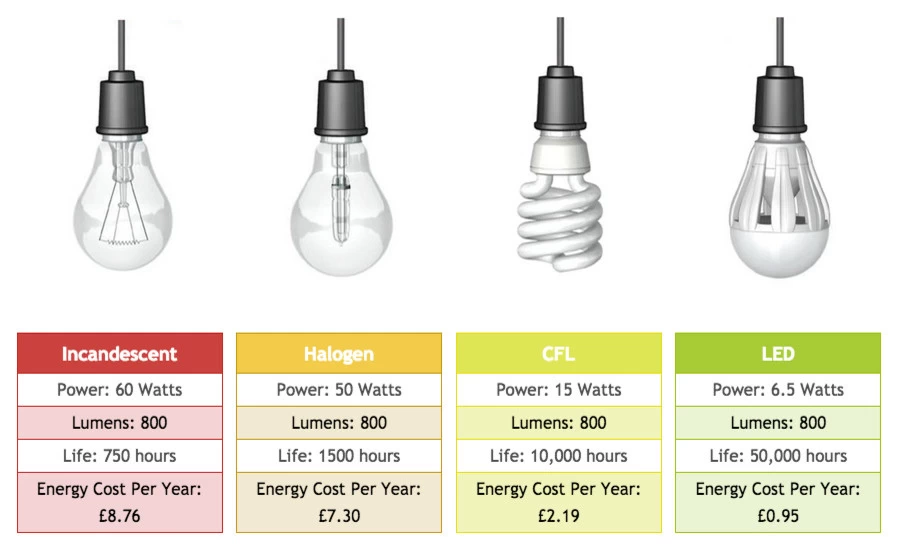
60W LED Comparable
A 9W LED bulb is a popular replacement for a 60W incandescent bulb, offering 800 lumens of brightness.
Perfect for general lighting.
75W LED Equivalent
A 13W-15W LED bulb provides 1200-1400 lumens, making it a suitable replacement for a 75W incandescent bulb.
LED Bulb Equivalent to 100W
A 100W incandescent has approximately 1600lm. If the luminous efficacy of LED bulb is 80-100lm/W. Then 16W-20W LED bulb equivalent to 100W incandescent.
150W LED Equivalent
For large rooms or industrial applications, a 30W+ LED bulb replaces a 150W incandescent bulb, providing exceptional brightness.
Incandescent to LED Bulb Conversion
Switching to LEDs is simple once you understand wattage and lumens. Here’s a quick conversion chart:
| LED Wattage | Incandescent Wattage | Lumens |
|---|---|---|
| 5W-7W | 40W | 400-500 lumens |
| 9W-10W | 60W | 800-900 lumens |
| 13W-15W | 75W | 1200-1400 lumens |
| 18W-20W | 100W | 1600-1800 lumens |
| 30W+ | 150W | 2400+ lumens |
LED vs Incandescent and Tungsten Bulbs Comparison
Energy Efficiency and Brightness
LEDs last 25 times longer and consume 75% less energy than incandescent bulbs.
Tungsten bulbs, in comparison, emit more heat than light, making them less effective.
Tungsten Bulb vs LED
- Energy Efficiency
Tungsten bulb: Luminous efficacy is extremely low (10–15lm/W), with 95% of energy used converted into waste heat and only 5% used for light.
LED: Their luminous efficacy is extremely high (80–150+lm/W), consuming only 1/6–1/10 the energy of tungsten bulbs.
LED win: They save over 85% on electricity costs at the same brightness. - Lifespan
Tungsten bulb: Average lifespan 1,000 hours.
LED: Average lifespan 25,000–50,000 hours. - Heat and Safety
Tungsten bulbs: Surface temperatures can reach over 200°C, posing a risk of burns or fire.
LEDs: Operating at low temperatures (surface temperatures < 60°C), significantly improving safety. - Cost
Tungsten bulbs: Low unit price ($1–$5), but extremely high electricity and replacement costs.
LEDs: Higher unit price ($3–$20), but offer a 90% long-term cost savings.
LEDs win: Payback within 2 years, offering superior long-term economics.

Selecting the Appropriate LED Wattage for Your Area
When choosing LED bulbs, consider the size and purpose of the space:
- Living rooms: Use 60W LED equivalents for soft, ambient lighting.
- Kitchens and offices: Use 100W LED equivalents for bright task lighting.
- Outdoor spaces: Use 150W LED equivalents for floodlights or security lighting.
LED Bulbs' Advantages: Longevity and Efficiency
Why Choose LED Light Bulbs?
- Energy savings: LED bulbs consume significantly less energy, reducing electricity costs.
- Long lifespan: LEDs can last up to 50,000 hours, minimizing replacements.
- Eco-friendly: Lower energy usage reduces carbon emissions.
LedRhythm Lighting Products
LedRhythm offers high-quality Industrial and commercial led lights. The luminous efficacy range is 120-200lm/W, and power can reach up to 2000W. Check out their full product line here.
Conclusion
When comparing traditional lamps with LEDs, the key consideration is the LED’s luminous efficacy (lm/W). The luminous efficacy of LEDs (80-150+ lm/W) is significantly higher than that of incandescent lamps (10-15 lm/W).
As a result, a low-wattage LED (8W) can provide the same brightness as a high-wattage incandescent (60W), significantly reducing power consumption. Remember: equivalent wattage is a measure of brightness, not power consumption; when choosing a lamp, pay close attention to the manufacturer’s “lm” rating.
People Also Ask
What is the equivalent wattage for a 60 Watt LED bulb?
A 60 Watt LED equivalent bulb consumes only 8-10 Watts while delivering the same brightness.
Can a 100 Watt incandescent bulb be replaced with an LED?
Yes, a 100 Watt LED equivalent consumes around 15-20 Watts and provides the same brightness.
Are low wattage LED bulbs as bright as incandescent ones?
Yes, thanks to their high lumen output, even a 4 Watt LED can match the brightness of a 40 Watt incandescent bulb.
Is the higher the LED light wattage, the better?
LED lights aren’t necessarily better when they have a higher wattage; rather, they’re best when they have the right brightness(lm). Lumens should be selected based on the lighting space, function, and brightness requirements.
If the lighting space is large and high brightness is required, a higher wattage LED light is better. Otherwise, glare will be severe and energy will be wasted.










